Generative Engine Optimization (GEO) marks the shift from SEO to GEO, becoming the operating system that determines which multi-location brands AI answer engines trust, cite, and recommend, not just which pages rank in traditional search.
Summary
Search is no longer a page of links. It is AI systems providing instant, conversational answers and showing only a handful of brands per question. For multi-location businesses, high rankings are now table stakes, not a guarantee of visibility. In fact, 44% of users now say AI-powered search is their primary source of insight, compared with just 31% who rely primarily on traditional search engines.
To win in 2026, you must give AI engines precise, machine‑readable facts about every location and every service. This article explains what multi-location brands need to unlearn from traditional SEO, what they must relearn for GEO, and how tools like Birdeye Search AI help deliver accurate data and grow your Share of Answer.
Table of contents
- Summary
- From SEO to GEO: How the rules evolved
- Why this shift from SEO to GEO matters in 2026
- What multi-location brands must unlearn
- The multi-location content dilemma: Depth vs. scale
- What brands must relearn to win with GEO
- The GEO Maturity Model for multi-location brands
- FAQs on the shift from SEO to GEO
- How Birdeye helps enterprises operationalize GEO
What is Share of Answer (SOA)?
Share of Answer (SOA) measures how often AI‑driven platforms (like ChatGPT, Google’s AI Overviews, Gemini, and Perplexity) choose your brand as part of their direct responses for a defined set of queries, journeys, or regions. Instead of asking “Where do we rank?”, SOA asks “How often are we actually mentioned or recommended when AI engines answer our customers?”
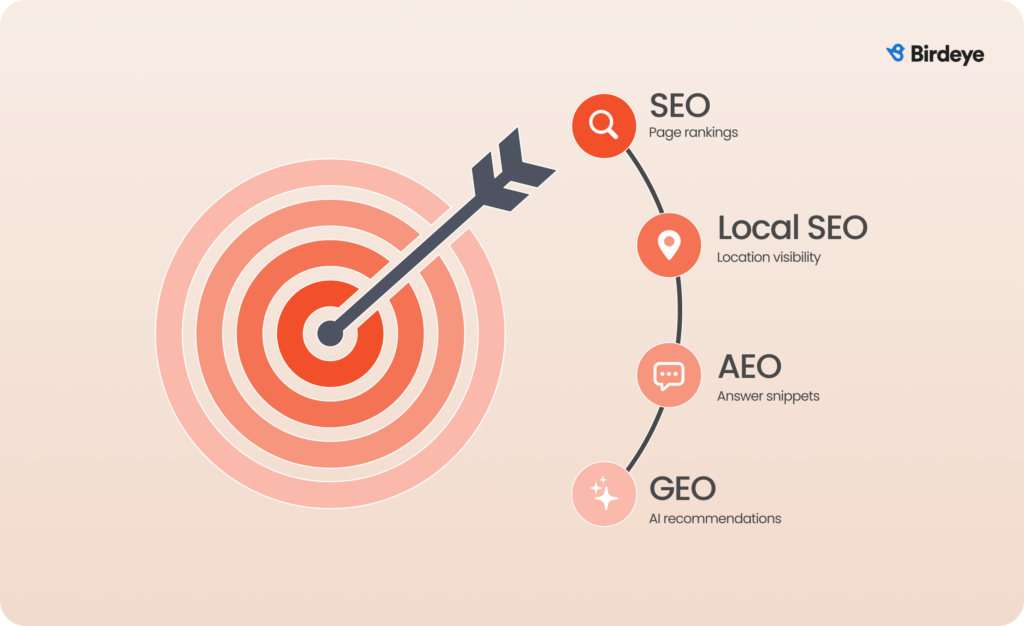
From SEO to GEO: How the rules evolved
For years, SEO meant improving how pages ranked in classic search results by optimizing content, technical health, and backlinks. Local SEO extended that playbook to individual stores and offices, focusing on “near me” searches, map listings, and NAP (name, address, phone) consistency.
As search engines began answering questions directly in featured snippets and People Also Ask boxes, Answer Engine Optimization (AEO) emerged. AEO is the practice of structuring content—summaries, FAQs, schemas, clear headings—so search systems can easily extract short, direct answers to common questions.
Generative AI has further accelerated this shift, with GEO focusing on the underlying facts, entities, and signals that large language models use to assemble full, conversational answers and recommendations.
For multi-location brands, GEO means connecting location data, reviews, content, and digital PR into one authoritative knowledge layer that AI engines can rely on. The more consistent, complete, and corroborated that layer is, the more often you appear inside generative answers instead of being silently replaced.
Why this shift from SEO to GEO matters in 2026
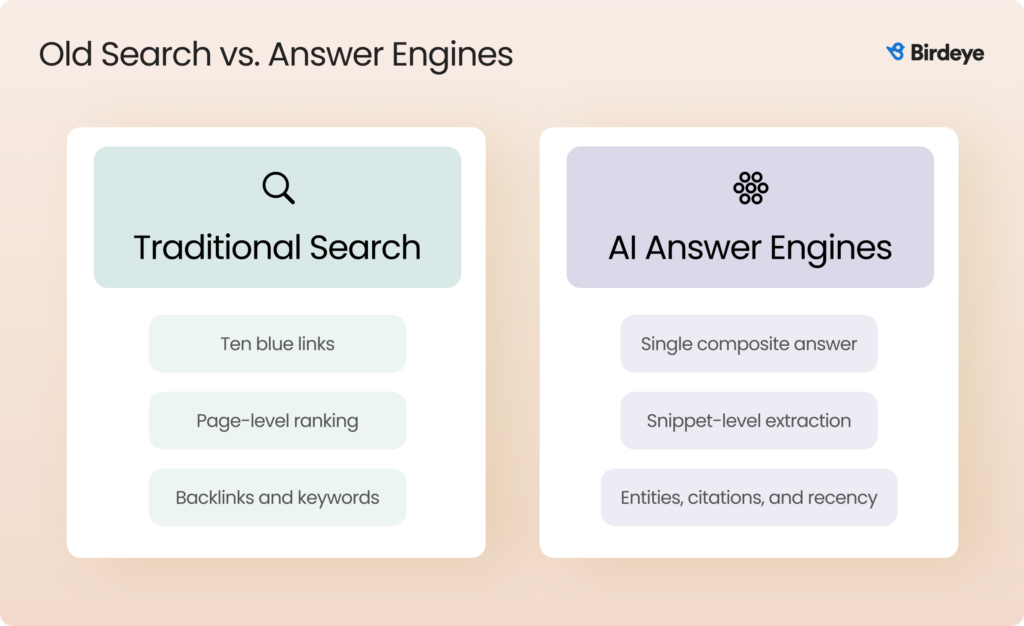
Search no longer stops at “ten blue links.” Today, AI systems pull from websites, profiles, news stories, reviews, and public data to synthesize a single answer for each user in each market. These systems act more like librarians or trusted advisors, weighing credibility, recency, and specificity before recommending a brand.
This shift makes entity accuracy, brand clarity, and cross‑source corroboration the new ranking factors for whether you are included at all. Your website is now just one of many sources AI evaluates. If your facts conflict across sources, or if competitors provide clearer data, AI engines may exclude your brand. That’s why your entire strategy—from website architecture to metrics—must change.
If an AI model “knows” your locations, services, and strengths with confidence, it is much more likely to include your brand in shortlists, map results, and recommendations. If your data is incomplete or inconsistent, it’ll either leave you out or fill the gaps with hallucinations, which can significantly damage customer trust.
For enterprises, this makes GEO a critical day-to-day focus area for data quality, content governance, and signal distribution across all locations. Multi-location brands are especially exposed because thousands of small data points – addresses, hours, services, pricing – must line up everywhere AI engines look, or confidence erodes fast.
What multi-location brands must unlearn
1. Ranking isn’t about visibility anymore
In the GEO era, ranking well in classic SERPs no longer guarantees visibility. There is now a weak overlap between what ranks and what AI engines choose to include in their answers. AI evaluates clarity, trust, and factual strength, not just keyword relevance.
A page can “rank” yet still be excluded from generative answers if:
- Its facts are unclear or inconsistent
- Competitors have stronger corroboration
- AI cannot easily extract precise information
For multi-location brands, this disconnect creates new risk. AI engines need accurate, location-specific details—services, hours, reviews, and attributes—to confidently surface a business in an answer. If any of these signals are missing or contradictory, visibility drops, regardless of traditional rank.
2. “Set it and forget it” publishing no longer works
The old pattern of publishing a page, gaining a few links, and revisiting it once a year is now risky. In today’s AI-driven search world, static content quickly becomes unusable. When pages aren’t updated, AI engines struggle to verify whether the information is still accurate. If models can’t confirm your details or find fresher signals elsewhere, they either guess or omit your brand entirely.
For multi-location enterprises, outdated information compounds quickly. Changes in hours, services, coverage, or pricing create inconsistencies that quietly lower AI inclusion rates. Content and location data must stay current, validated, and tightly aligned with real‑world operations so AI systems can trust and reuse them.
3. Link building isn’t the game—Digital PR is
Classic SEO relied heavily on backlinks and anchor text. But AI engines don’t evaluate links the same way. They look for trusted sources, consistent narratives, and cross-platform corroboration when deciding which brands to include in answers.
From Reddit threads, Quora answers, and local news articles to industry review sites and YouTube transcripts, all influence how AI models decide which brands are credible for specific topics and locations.
It’s time for multi-location brands to stop chasing links and start investing in digital PR that builds trust and clarity. The brands that succeed in GEO are the ones that share accurate, fact-rich stories across all the sources that AI reads.
4. Incomplete location profiles break AI confidence
AI engines rely on clear, consistent, and complete location data to include a business in answers. When profiles are missing details or contain conflicting information, AI confidence drops, and so does visibility. In categories such as healthcare, financial services, and retail, incomplete or conflicting profiles can be worse than no profile at all because they reduce AI confidence.
For multi-location enterprises, perfect data hygiene across all platforms is non-negotiable. The most critical fields include:
- Core identifiers: Name, address, phone number, and URL.
- Operational details: Hours, appointment rules, service coverage.
- Commercial details: Pricing ranges, insurance or payment types, and offers.
- Descriptive attributes: Categories, specialties, neighborhoods, and key differentiators.
When AI models identify contradictions across your site, map listings, and third-party directories, they often downgrade your data and elevate competitors that appear more consistent.
5. Governance gaps and siloed workflows
Most large companies still divide key responsibilities (SEO, PR, operations, etc.) among separate teams using different tools. The website is one team’s job, reviews are another’s, and so on. No single team owns the brand’s unified presence in AI answers. This fragmentation slows updates and lets conflicting information spread.
Without a clear owner for GEO, no one is accountable for winning the “Share of Answer” or fixing incorrect AI responses. Closing this gap requires clear governance, centralized standards, and cross-functional processes to ensure every location remains accurate and answer-ready.
The multi-location content dilemma: Depth vs. scale
Multi-location brands constantly struggle to balance creating unique local content with the need to produce content quickly. Simple, repetitive, or copied pages might please old SEO rules, but AI engines ignore them. Why? Because they don’t show real expertise or local relevance.
AI wants rich, unique content—things like local details, staff expertise, and unique reputation signals. If every page reads the same, the AI can’t tell your branches apart, and your visibility suffers.
The solution is layered content: a shared core brand message plus deep, unique details about what each branch offers, who it serves, and why it matters in that specific community. Simply put, for GEO, quality beats quantity. Five hundred detailed, unique location pages will easily outperform 5,000 thin, cloned pages.
What brands must relearn to win with GEO
1. Build answer-ready content architecture
AI engines prioritize content they can parse, verify, and recombine. That means multi-location brands need a content structure designed not just for users, but for machines that assemble answers.
Answer-ready content has three qualities:
- Clarity: direct statements, clean hierarchy, precise facts
- Structure: headings, lists, FAQs, rich schema
- Verification: citations, reviews, and consistent corroboration across sources
Here’s how you can create AI answer-ready content:
- Lead with the answer: Start with the answer in the first 40–60 words of each key section so models can see the core point immediately.
- Increase fact density: Aim for at least one useful data point, example, or concrete claim every 150–200 words so AI has something specific to reuse.
- Use semantic hierarchy: Use clear headings (H1 → H2 → H3) so both humans and AI can map content to specific questions.
- Break up narratives: Convert long paragraphs into bullet points, steps, and FAQs to improve readability.
- Add proprietary proof: Use internal data, examples, and metrics to strengthen authority.
- Add structured data: Use Organization, LocalBusiness, Product, Service, FAQ, and Review schema to make facts machine-readable.
- Localize meaningfully: Include location-specific services, staff expertise, and reputation signals, not just city-name inserts.
- Write for entities, not just keywords: Name brands, services, locations, and attributes the way customers actually search.
When content is structured for both humans and AI, inclusion in generative answers increases across locations.
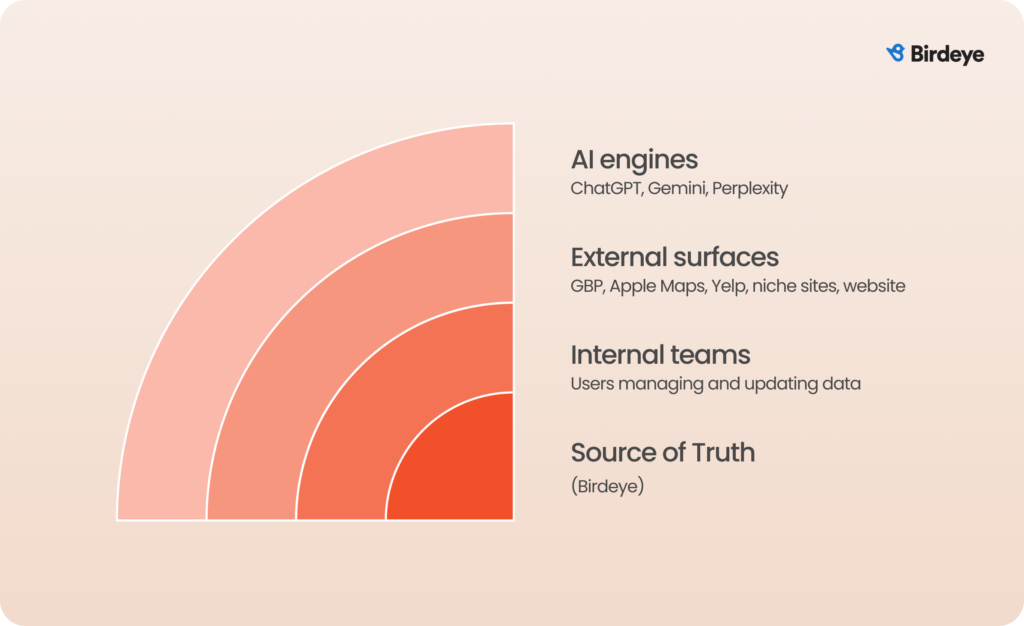
2. Be present where AI actually looks
AI engines don’t rely on a single source. They triangulate information across directories, review sites, social platforms, news coverage, local listings, and your own web pages. Visibility depends on showing up consistently across these surfaces so AI can verify your facts and understand your authority.
Below are the key sources where AI looks for validation:
- Local and vertical media that cover openings, expansions, and partnerships
- Forums and Q&A platforms like Reddit and Quora
- Industry review platforms and aggregators
- YouTube videos and transcripts that explain services and show locations
- Map data and public datasets that confirm categories and service areas
Here are a few tips to improve your AI visibility:
- Publish localized PR: Create market-specific stories that clearly reference your brand, services, and individual locations.
- Produce YouTube explainers: Use strong titles, chapters, and captions so AI can easily interpret your service content.
- Participate in communities: Offer helpful, non-promotional insights in authoritative forums tied to real problems and local contexts.
- Activate reviews at scale: Use a platform to drive, respond to, and highlight reviews that reference services, outcomes, and neighborhoods, turning UGC into structured GEO signals.
Reviews and user-generated content matter because they are fresh, specific, and trusted, which makes them ideal material for AI engines to rely on when choosing which local brands to name.
3. Maintain machine-readable local knowledge at scale
AI engines want one clear, consistent set of facts for every location. When details differ across directories, landing pages, or schema, they lose confidence and may exclude the location from answers. This makes maintaining machine-readable accuracy at scale a core operational requirement for multi-location brands.
Here’s how you can stay AI-ready:
- Standardize location data: Centralize location data into a structured source of truth with clear ownership and audit trails.
- Update continuously: Automate updates from that source to Google Business Profiles, Apple Maps, Yelp, and niche directories using enterprise workflows.
- Use appropriate attributes: Enrich descriptions with specific attributes (“same-day appointments,” “same-day deliveries,” “mid-market B2B payments,” etc.) that align with real search behavior.
- Monitor and fix AI hallucinations: Use a structured testing program rather than waiting for customers to report issues with AI responses.
- Run regular tests: Run tests across ChatGPT, SGE, Gemini, and Perplexity to see how often and how accurately your brand appears.
- Validate externally: Confirm that third-party listings, reviews, and local citations match the brand’s first-party data.
Machine‑readable consistency gives AI engines the confidence to surface each location reliably across answer engines and AI Overviews, rather than guessing or skipping it.
4. Make Share of Answer your core KPI
Share of Answer is the percentage of relevant AI responses that mention or recommend your brand for a specific query set, persona, or region. It aligns with how customers now discover and choose brands through AI overviews, chat experiences, and map answers.
To operationalize this, enterprises should track:
- Query inclusion rate: How frequently your brand appears in AI Overviews and answer engines for priority queries.
- Citation accuracy: Whether AI systems use your information correctly and reference the right location details.
- Location-level inclusion: Which branches appear consistently—and which ones drop out due to missing or unclear data.
- Competitor presence: How often rivals surface in the same AI summaries or replace you entirely.
- Sentiment influence: How review quality and freshness affect your likelihood of being included.
With these metrics, Share of Answer becomes a practical KPI that directly links visibility to operations, content quality, and data consistency.
Pro tip: Create a GEO dashboard that shows these metrics by region, vertical, and service line so leadership can see exactly how GEO work turns into visibility, traffic, and revenue.
Over time, SOA should replace rank tracking as the primary health metric for how well GEO is working across journeys and regions.
5. Fix governance and workflows for GEO
GEO only works when teams share ownership of the signals AI engines evaluate. Today, most enterprises still separate SEO, CX, operations, analytics, and PR, creating gaps that lead to inconsistent data, slow updates, and unclear accountability.
To support GEO, enterprises need:
- Centralized standards: A single source of truth for location data, service descriptions, schema, and content guidelines.
- Clear roles: Defined responsibilities across SEO, CX, operations, and PR so updates flow consistently across systems.
- Cross-functional cadence: Regular alignment between teams to review AI inclusion trends, citation accuracy, and gaps.
- Coordinated updates: Changes to hours, offerings, messaging, or attributes must sync across directories, pages, and schema simultaneously.
- Governance enforcement: Use tools, workflows, and audits to ensure every location stays accurate and machine-readable.
Fixing governance is the key. It’s how you ensure all your efforts work together so AI engines always receive consistent, trustworthy signals.
6. Run a 60–90 day GEO pilot program
Enterprises don’t need a full overhaul to see the value of GEO. A focused 60–90 day pilot can reveal how AI engines interpret your data, where inconsistencies appear, and which updates drive the biggest visibility gains.
Here’s how you can run a fast, effective 5-step GEO pilot:
- Choose the scope: Pick one region or vertical where AI visibility matters most, and you have internal champions.
- Set a baseline: Measure current SOA, citations, review health, and AI-referred conversions for that scope.
- Apply the four GEO pillars: Roll out answer-ready content, multi-surface presence, strong data hygiene, and clear governance for the pilot area.
- Measure and refine: Track changes in SOA, citations, reviews, and conversions over 60–90 days and refine tactics as you learn.
- Turn results into a roadmap: Use uplift, lessons, and process changes from the pilot to design an enterprise-wide GEO roadmap with clear phases, roles, and investment.
A short pilot shows how quickly clarity, structure, and corroboration change your Share of Answer, creating a concrete business case for scaling GEO across all locations.
The GEO Maturity Model for multi-location brands
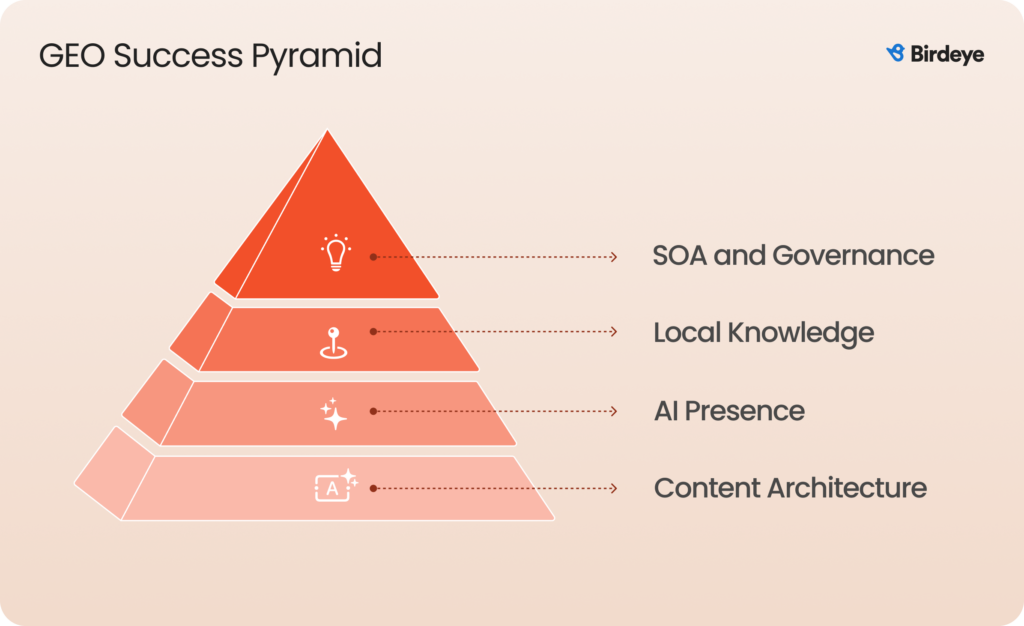
To turn GEO from theory into an operating model, it helps to know where you stand today. The GEO Maturity Model describes four stages enterprises typically move through as they adapt from traditional SEO to a GEO discipline.
Level 1: Basic presence
Brands at this level have minimal AI visibility. Data is inconsistent, location pages are thin or templated, and reviews are unmanaged. AI engines struggle to understand the brand or trust its facts, leading to low inclusion in answers.
Level 2: Structured SEO + Early GEO
Location data becomes more consistent, schema is introduced, and review management improves. Some pages start ranking for answer-friendly queries, but visibility remains uneven because content depth and corroboration vary by location.
Level 3: GEO operationalized across teams
SEO, CX, operations, and PR work from shared data standards. Location pages are enriched with local proof points, FAQs, and machine-readable structure. Review signals are strong and consistent. AI engines begin including the brand regularly across many queries and locations.
Level 4: Predictive GEO + Brand authority
The brand maintains complete, corroborated information across all locations and anticipates search behavior before it appears. Predictive insights shape content, PR, and CX decisions. AI engines consistently surface the brand in answers because its entity signals are clear, verified, and trusted.
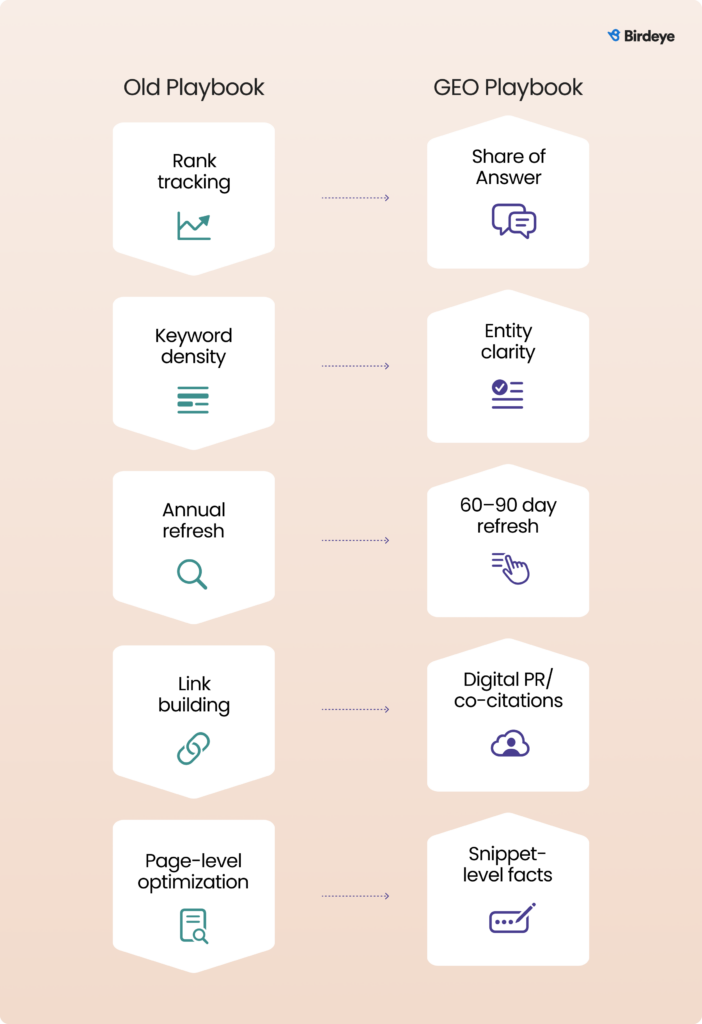
GEO unlearning checklist: What to leave behind and what to adopt
The GEO success depends as much on unlearning outdated SEO habits as it does on adopting new ones. Use the following checklist as a simple guide when reviewing your current SEO programs:
Stop prioritizing:
- Rank tracking as the primary success metric
- Keyword density and long, generic evergreen pages
- Annual “big bang” refreshes
- Generic link-building campaigns with low-quality sites
- Thin, templated location pages with only city-name swaps
Start prioritizing
- Share of Answer and AI citation frequency by engine and region
- Entity clarity, structured data, and fact-dense, snippet-ready content
- Regular 60–90-day refresh cycles for high-intent and location pages
- Digital PR, reviews, and co-citations across trusted local and vertical sources
- Rich, differentiated location content that balances consistent templates with real local depth
Use this checklist alongside strong governance, a GEO pilot, and platforms like Birdeye Search AI to build an operating system that AI search engines can trust, leaving outdated SEO habits behind.
“Birdeye’s Search AI gives multi-location brands the power to optimize visibility, sentiment, and engagement across all platforms.”
— Adam Dorfman, AVP of Product Management and AI Search, Birdeye
Be the #1 answer on all AI engines
Want to see the impact of Birdeye on your business? Watch the Free Demo Now.
FAQs on the shift from SEO to GEO
GEO focuses on the factual, machine-readable signals that AI models use to generate answers and recommendations—such as entity clarity, citations, and structured data—rather than just improving page rankings.
Key metrics include Share of Answer across priority journeys, entity presence in AI responses, citation frequency by engine, AI-referred conversions, and review signals like volume, recency, and topic coverage by location.
GEO usually sits at the intersection of marketing, CX, and operations, with one designated owner responsible for data integrity, AI visibility, and performance measurement across all locations.
AI engines reduce or remove recommendations when they detect incomplete, outdated, or conflicting location data, because that lowers their confidence that you are the right answer for the query and geography.
High-intent pages should be reviewed every 60–90 days, with location pages updated more often when hours, services, inventory, offers, or compliance details change.
Rankings still matter for some discovery paths, but are less predictive of AI visibility than accurate citations and strong entities; only a small share of AI overview results overlap with classic organic rankings in many categories.
Maintain consistent, validated data across websites, profiles, and directories, and run an AI Testing Lab with synthetic personas that regularly check answers and trigger structured remediation workflows.
GEO builds on your existing SEO work—content, technical health, and authority—while shifting the focus toward how easily AI can extract and trust answers and how often you appear in AI responses.
How Birdeye helps enterprises operationalize GEO
GEO requires accurate data, answer‑ready content, and coordinated workflows across hundreds or thousands of locations. Birdeye Search AI connects those pieces so enterprises can treat GEO as an operating model, not just a one‑off project, without rebuilding their tech stack from scratch.
Here’s what Birdeye offers:
1. A unified source of truth for local and reputation data
Birdeye integrates location attributes, listings, and reviews into a single platform that syncs with Google, Apple, Facebook, and key directories. This gives AI engines a consistent, up-to-date view of every location, reducing the risk of conflicting signals.
2. AI visibility testing and Share of Answer analytics
With Birdeye Search AI, enterprises can run structured tests across multiple AI engines, see where and how often they are mentioned, and benchmark Share of Answer by query set, persona, and region. This turns GEO from a vague idea into a measurable, repeatable practice tied directly to Share of Answer and revenue‑relevant KPIs.
3. Answer-ready content and review workflows at scale
Birdeye helps teams standardize templates for location pages and profiles, automate review generation and responses, and push structured updates across channels. This makes it easier to maintain answer-ready content, strong reviews, and accurate attributes across thousands of locations from a single place.
4. Governance and automation for GEO workflows
Roles, approvals, and SLAs can be enforced in Birdeye, ensuring only the right people can modify critical fields such as hours, services, and legal disclosures. Automation handles distribution and sync, while audit trails show who changed what and when, which is essential for regulated industries and for scaling GEO across complex organizations.
Enterprises that act now will not only adapt to AI search but will also help shape how those engines understand their entire industry and decide which brands lead it. Birdeye Search AI is built to help multi-location brands make this critical shift with confidence.

Originally published